Travel safe in North America
North America is the second largest continent in the world, and the fourth most populated continent with almost 529 million inhabitants. The continent consists of two large countries: Canada and the Unites States.
Climate
A large number of climate zones can be found in the Unites States and Canada. The northern part of the continent, Canada and the state of Alaska, is characterised by cool continental climates, tundra climate and snow and mountain climates. Temperatures above 20 degrees Celcius are rare, in the wintermonths, there is an almost continuous frost (from light in southwest Canada to very severe in the Arctic).
The climate is significantly warmer in the United States. There are some very dry areas (Nevada and Arizona) and some very sunny parts (California) and a very wet northwest coast.
Area: 19,814,345 km²
Population: 362,249,471
Climate: Varied
Tropical diseases in North America
Dengue
Yes, dengue occurs in North America.
Yellow fever
No, yellow fever does not occur in North America.
Malaria
No, malaria does not occur in North America.
West Nile virus
Yes, West Nile virus occurs in North America.
Zika
Yes, zika occurs in North America.
Dangerous animals in North America
When it comes to dangerous animals, you most likely think of preditors in Africa, venemous snakes in the Middle East and deadly sea creatures in distant oceans. However, in Central America, you can also encounter several dangerous creatures. Read the information below to know what to look out for and be prepared when travelling.
Ticks
Ticks live in forests, dunes, heathland, sheltered meadows, parks and gardens. Particularly in tall grass or dead leaves. They also live on pets, wild animals, birds and cadavers. They attach themselves to passing animals and people. Ticks become active when the temperature rises above 7 degrees Celsius.
Ticks can transmit diseases, such as Lyme disease. Prevent a tick bite with Anti-Insect and be sure to bring an (impregnated) travel mosquito net when you’re staying in a forested area. Insect repellent socks are recommended for hiking, as the ticks come up from below.
Have you been bitten? It is important to remove a tick as soon as possible, within 8 hours, with a tick remover. Do not sedate the tick with alcohol nor heat it with a cigarette. The tick will give off pathogens through its saliva. You can disinfect the bite with alcohol. The risk of infection will remain minimal when the tick is removed within 8 hours.
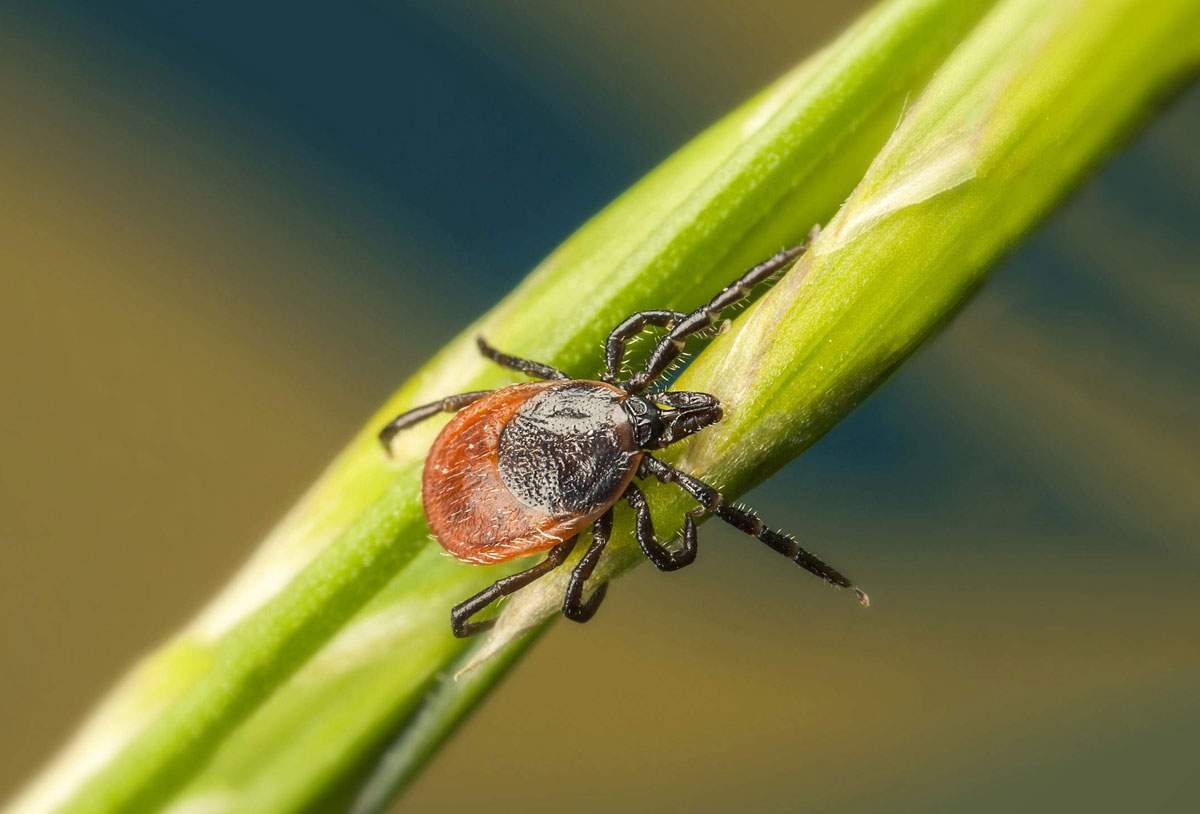

Ticks (Ixodida)
Mosquitoes
Watch out for mosquitos if you’re travelling to Florida, the Bahamas or Hawaii in the summer months. Mosquitoes that transmit dengue can occur. Always protect yourself by sleeping under a mosquito net, using Anti-Insect DEET and wearing insect repellent socks. Have you been bitten? Use a venom extractor to remove the venom. This prevents the venom from spreading through the body. Always consult a doctor immediately, should you have any of the symptoms of the diseases.
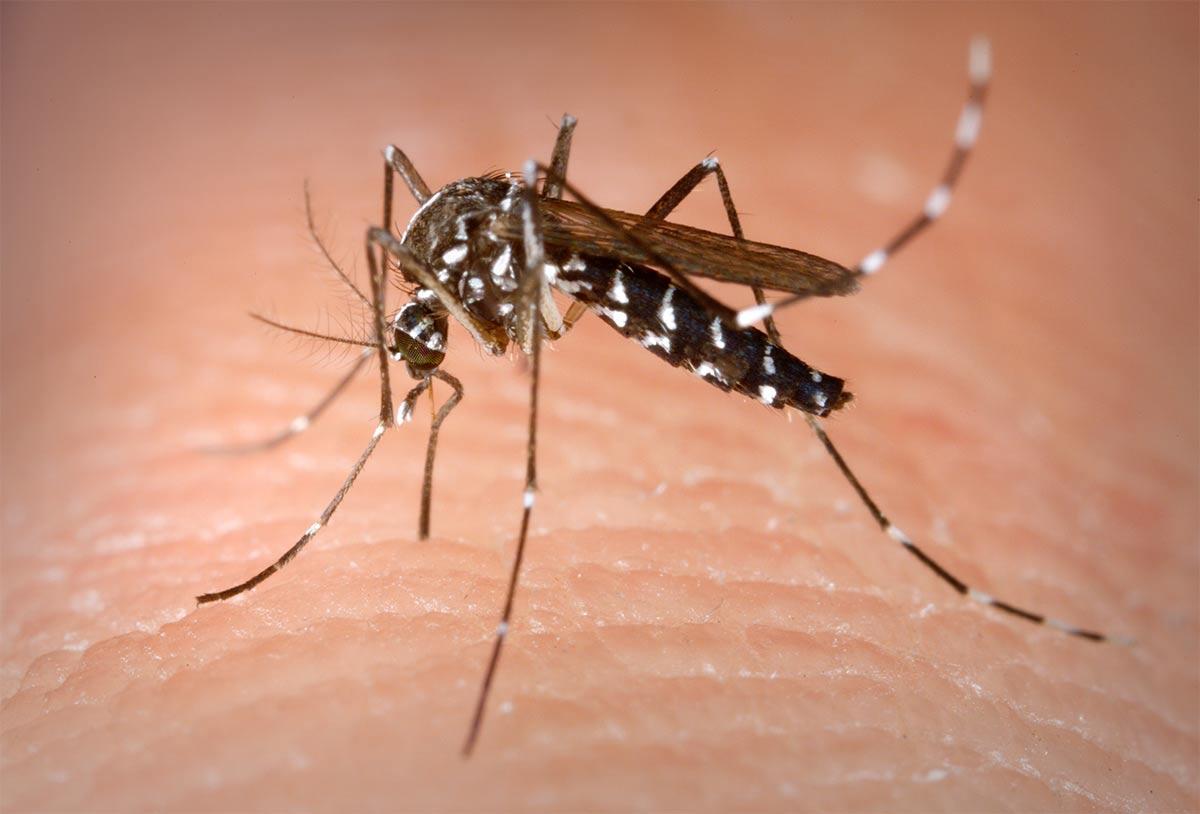

Mosquitoes (Nematocera)
Bears
In North America there are three types of bears: the black bear, the brown bear and the polar bear. The grizzly bear falls under brown bears and can be recognised by the hump on its back and its long claws. Bears look incredibly cute, but don’t forget they are wild animals and you need to keep your distance. Here are a few handy tips and some advice:
- Do not leave food or leftovers at your camping spot or picnic place, during your stay and when you leave.
- Ensure that your presence in nature is heard naturally. This prevents unexpected confrontations by being silent.
- Ensure that your cooking utensils are thoroughly cleaned.
What to do when you unexpectedly encounter a bear?
- Stay calm. Do not run (bears can run a lot faster than humans). While talking, walk away calmly while keeping an eye on the bear without making eye contact.
- Give the bear space, so he has an escape route.
- Carry children and stay in a group.
How do you recognize an aggressive bear?
- Swings its head from left to right.
- Makes growling, moaning, panting sounds.
- The ears lie flat on the head.
- Stamps feet with front legs on the ground.
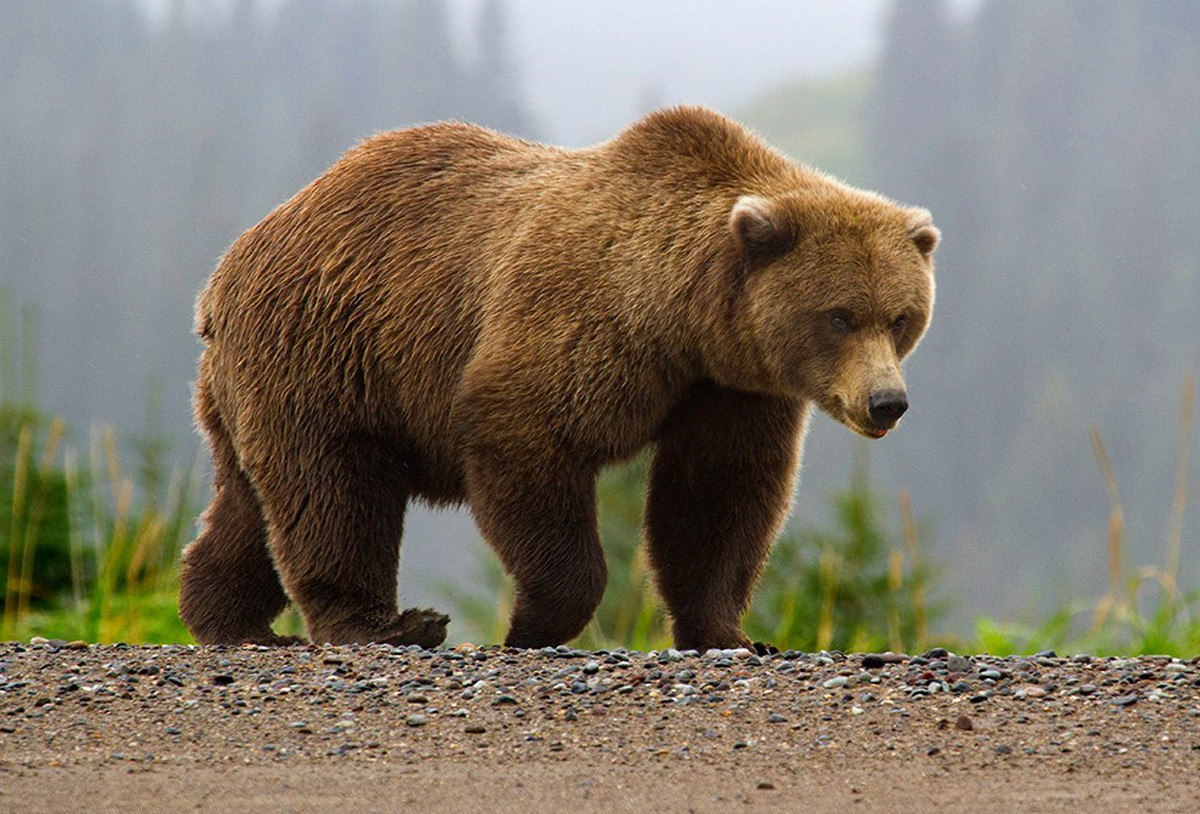

Grizzly bear (Ursus arctos horribilis)
Deer
In America, watch out for deer, especially the white-tailed deer. They have been known to jump out in front of cars, which can have nasty consequences. Pay attention to signs on the road warning you for deer in the area.
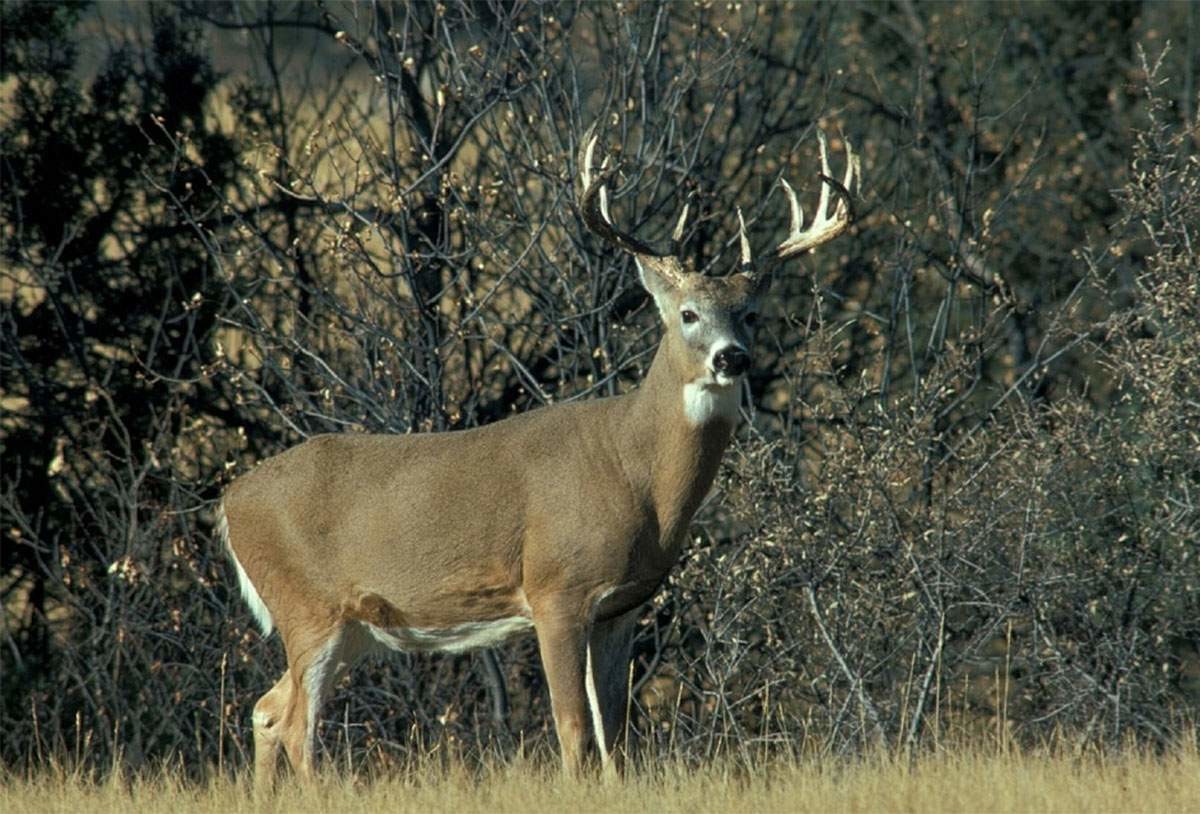

White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus)
What to pack




Good to know
Vaccinations
Vaccinations are usually not necessary when travelling to North America. If you’re going to Florida, the Bahamas and Hawaii in the summer months, be sure to protect yourself against mosquitoes. There are mosquitoes that can transmit dengue. Consult your local health service for advice.
Visa
When you’re travelling to North America, you will need an ESTA and/or ETA. This application should be completed online and is your own responsibility. The application must be completed at least 72 hours before departure and also applies to babies and children. In most cases, ESTA/ETA will confirm approval for travel without a visa.
Water
Tap water is safe for drinking in countries in North America.
Language
Although the United States do not have an official language, English is the national language, because it is the mother tongue for roughly 82% of the population. Canada is officially bilingual: people in Canada speak English and French.